1. Overview
-
FMCSA (Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration):
A federal agency under the U.S. Department of Transportation (USDOT). It sets nationwide safety regulations for commercial motor vehicles (CMVs), primarily focused on interstate commerce. -
NYSDOT (New York State Department of Transportation):
The state agency that enforces state-level regulations for trucking, including both intrastate (within NY) and some aspects of interstate operations in NY. NYSDOT can have stricter rules than FMCSA.
2. Key Areas of Comparison
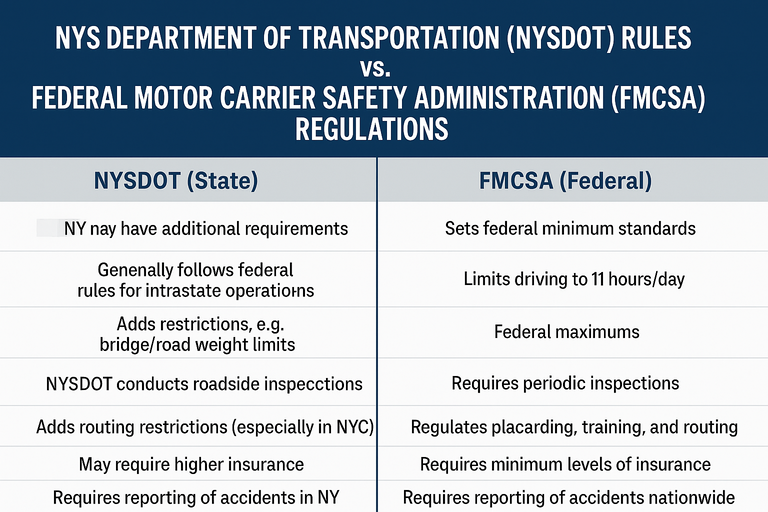
| Area | FMCSA (Federal) | NYSDOT (State) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Commercial Driver’s License (CDL) | Sets federal minimum standards for CDL issuance and endorsements. | NY may have additional requirements, like certain medical certifications or special endorsements. | Drivers must meet both federal and state CDL requirements. |
| Hours of Service (HOS) | Limits driving to 11 hours/day, 14-hour work window, 60/70-hour weekly limits. | NY generally follows federal HOS rules for intrastate operations but can have additional state-specific rules for logging, such as electronic logging device (ELD) mandates. | NY enforces ELD usage and can conduct inspections. |
| Vehicle Size & Weight | Federal maximums: 80,000 lbs gross vehicle weight, specific length limits for combination vehicles. | NY has additional restrictions, e.g., bridge and road weight limits, and special permits for oversized/overweight loads. | Truckers must check both federal limits and NY-specific limits. |
| Safety Inspections | FMCSA requires annual inspections, roadside inspections, and periodic brake/vehicle safety checks. | NYSDOT conducts roadside inspections, NY Safety Rating Program, and vehicle compliance checks. | NYSDOT inspections may be more frequent, particularly in congested urban areas. |
| Hazardous Materials (HazMat) | FMCSA regulates HazMat transport, including placarding, training, and routing. | NY adds state-specific routing restrictions (especially in NYC), permitting, and safety regulations. | NY may prohibit HazMat trucks on certain bridges, tunnels, and streets. |
| Insurance & Financial Responsibility | FMCSA requires minimum levels of liability insurance based on cargo and vehicle type. | NYSDOT may require higher insurance or surety bonds for intrastate carriers. | NY can suspend operations if insurance proof isn’t adequate. |
| Accident Reporting | FMCSA: CMV accidents must be reported within 24 hours to FMCSA/appropriate authorities. | NYSDOT requires reporting of accidents in NY state and maintains its own crash reporting database. | Drivers must comply with both reporting requirements. |
3. Key Takeaways
-
Federal rules are minimum standards. States like New York can impose stricter regulations.
-
All commercial trucks in NY must comply with both sets of rules, or risk fines, inspections, and license suspension.
-
Intrastate vs. Interstate:
-
Interstate trucking: FMCSA rules primarily govern, but NYSDOT enforces when trucks operate in NY.
-
Intrastate trucking: NYSDOT rules are fully applicable, sometimes exceeding FMCSA standards.
-
-
Urban considerations: NY imposes additional restrictions in NYC, such as low-emission zones, truck routes, bridge/tunnel limits, and parking regulations.